I was planning for a vacation rental and began was searching online. And, it only took maybe a few minutes for all the social media sites to get this information before they started flashing ads. When these sorts of events initially started happening, it was tough for a majority of consumers, but it has become so common and they all have gotten used to it over time. But are consumers really happy with such indiscriminate sharing and analyzing of data?
In the push to personalize customer experiences and offers, organizations are loading up on consumer data and using artificial intelligence (AI) to develop customer profiles and predict behavior.
The application of AI to massive quantities of personal consumer data has raised apprehensions about data security and artificial intelligence ethics. Ethics concerns include everything from surveillance and behavior manipulation to bias and opacity.
Organizations need to think through these issues and take measures to address them. Without standards in place, teams may slap together inadequate solutions or completely ignore issues, leading to creepy customer experiences and maybe even litigation. As an HBR article aptly put it, "In this environment, data and AI ethics are business necessities, not academic curiosities.”
AI can transform how call centers operate and deliver CX. But it needs to be used ethically and customer data needs to be safeguarded. Developing standards upon the initiation of AI projects will help ensure you're doing the right things for your customers and your business.
Why contact center AI is important and inevitable
Artificial intelligence has permeated contact centers, enhancing CX and making core processes more efficient and accurate. Contact centers have always been pressured to deliver great service while adhering to strict budgets. Artificial intelligence is the tool to help them meet both goals.
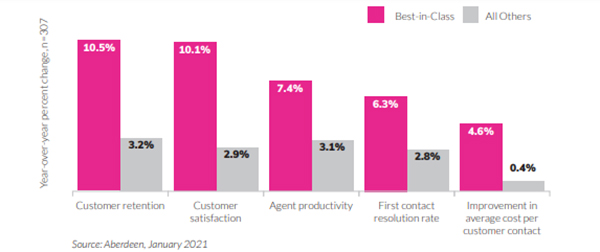
Aberdeen research revealed that high AI adopters have better business results - such as higher customer retention and agent productivity - than lower AI adopters.
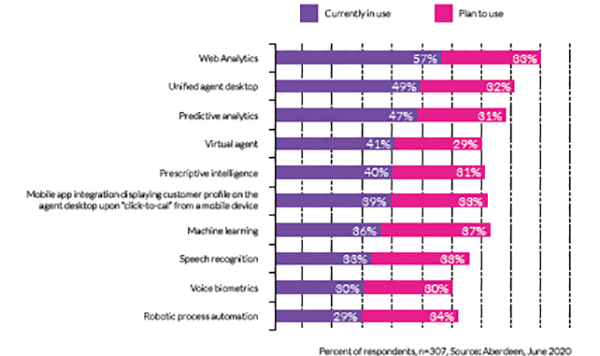
Additionally, most businesses already use artificial intelligence in their contact centers or plan to invest in AI in the near term. For organizations to successfully compete, AI is inevitable.
Here are some examples of how artificial intelligence solutions can give contact centers a competitive edge.
Automation
AI-powered bots can be the extra pair of helping hands many agents wish for. By one estimate, agents spend 14% of their time looking for information. Just think about what that does to handle times and labor costs! Bots can listen to and understand conversations, enabling them to quickly retrieve relevant knowledge base content for agents. And they can take things a step further by also suggesting the next steps.
Additionally, bots can perform administrative tasks for agents, such as documenting calls and completing transactions in back-office systems. This decreases handle times, increases agent capacity, and improves data accuracy. Plus, freeing up agents from mundane tasks allows them to better focus on creating loyalty-building rapport with customers.
Agent augmentation
When contact centers need to ramp up capacity, it can be expensive to just hire a bunch of new agents. Plus, businesses are having difficulty finding qualified candidates, and new agents take a while to get up to speed.
Customer-facing chatbots and virtual agents or a much more evolved IVR or voice bot can augment capacity by providing effective customer self-service. Empowering customers to solve their own simple problems reduces the number of interactions that need to be handled by agents. Customers value self-service - Gartner found that 70% of customers use self-service channels during their resolution journey. Self-service is particularly popular among millennials. And older consumer groups, who had to embrace technology during the COVID lockdowns, are also likely candidates for self-service.
Customer-facing bots leverage natural language processing (NLP), a form of artificial intelligence, to understand human language and intent and respond to people conversationally. Those that use machine learning can even get smarter with time and use. Bots are available 24/7 and can provide satisfying service. But they need to be designed correctly and used for the right tasks in order to not deliver creepy experiences.
Intelligence and insights
Artificial intelligence makes core contact center applications smarter and more accurate, resulting in improved operations and CX. When workforce management (WFM) solutions use AI, forecasts are more accurate and schedules improve with every run. AI can also be used to route customers to agents with whom they're likely to make a strong connection - a creative way to personalize experiences.
Artificial intelligence is particularly good at analyzing massive amounts of data to identify patterns and create insights. Interaction analytics tools leverage this capability by analyzing every contact from every channel and providing information about contact drivers, emerging problems, customer sentiment, and more. These insights allow contact center leaders to provide proactive customer service and pinpoint areas for improvement.
What are the concerns - security and ethics

These AI capabilities come with a responsibility to use artificial intelligence ethically and protect customers' data and privacy. Failure to do this can result in the catastrophic loss of customer trust. Below is a discussion of how AI initiatives can go wrong and get a little creepy.
Data privacy
Sometimes AI initiatives involve the acquisition of data businesses wouldn't normally have. For example, a retailer would have all the information about their customers' relationships and transactions with the business from their own systems. An AI project might add additional customer insights by getting data from unconventional places. So, does the retailer really need that extra information? Hard to answer.
Organizations need to find the right balance between having too much and not enough customer data. Consumers value personalized offers and experiences, which are at risk if the business doesn't have enough information. On the other hand, if a business uses too much information in an obvious way, it can feel like creepy surveillance.
Two big tech companies were under facing big lawsuits recently for data privacy issues. These cases demonstrate that consumers are willing to fight back when businesses misuse their private data. Violations can come with a hefty price tag.
Data security
Did you know that 37 billion records were compromised in 2020? And that data security breaches cost companies an average of $3.86 million in IT costs and lost revenue? That's probably why AI adopters ranked cybersecurity risks as their top concern.
Companies that are required to follow industry security standards, like PCI and HIPAA, need to apply those same standards to their AI data, including training data. If the AI solution includes an expansion of customer data, it does expand the scope for security creep.
Businesses implementing artificial intelligence have a responsibility to ensure customer data is secure. It's the right thing to do, plus nothing will kill customer trust quite like a data breach.
Bias
On the surface, it may not seem possible that artificial intelligence, which runs on logical algorithms, could be biased, but there are a couple of ways bias can creep in. First of all, there is a possibility that the algorithm is unintentionally biased. Secondly, bias can also be introduced through training data. Certain forms of AI have to be "trained" by analyzing huge amounts of data. This allows the machine to identify patterns and learn to make decisions and predictions. Many companies use historical data to train their AI, which can be a problem if their past practices were biased. As an example, a few years ago, one of the leading tech companies implemented AI to screen job candidates. But they found that the solution was discriminating against women. The tool was trained using resumes of past job applicants, who were disproportionately men. It learned to favor words like "executed" and "captured," which men tend to use more than women on their resumes. Women were screened out as an unintended consequence. Also, the training data could come from a certain type of persona in IT or business function that could be limited in the training data set since they are narrow in how they see the user perspective.
Empathy versus getting things done
Most AI chatbots are programmed to execute routine, narrowly defined tasks. They're all business with maybe a little artificial personality thrown in. That can be fine if the bot is just helping you change your password or taking your pizza order, but there are times when some empathy would be appropriate.
Imagine you use a bot to file a claim for a terrible car accident you were just in. You're shaken up and need a soft touch, but the bot has been programmed to be perky or maybe it's mechanically all business. That would be a little creepy and a painful reminder that you're dealing with a robot. You might decide to call and talk to a human if this ever happens again.
A robotic interaction with a customer who needs some TLC will create a terrible experience. Best case - the customer will never use the bot again. Worst case - you lose the customer.
Human/bot relationship
Losing your job to a bot would be creepy, among other things. It may be a reality for some workers in some industries, but for now, customer service agents are safe. There's been speculation that human agents would become obsolete, but the reality is that 41% of businesses will increase the number of agents in the coming year.
Although AI won't replace agents, it will eventually change the nature of their jobs. As bots help customers solve more of their simple problems, the mix of interactions that make it through to agents will be more complex. This means agents will need to shift from performing routine transactions to solving more complicated problems. This should improve agent engagement, as they'll be performing more interesting work and adding more value to the organization.
How to mitigate AI ethics and security concerns

The issues described above can be challenging, but they're certainly not insurmountable. The benefits of AI are worth the effort of mitigating the risks. Here are some things you can do to ensure your AI solutions are ethical, secure, and not at all creepy.
Involve IT
Your IT team will likely be part of any AI initiative, but make sure the right skillsets are represented. Your data security team should be involved from the beginning and tasked with developing a secure data plan. Because you may have a lot of additional data on your hands, safeguarding it needs special attention. Make sure the plan includes securing sensitive training and testing data. Additionally, ensure integrations with other data stores are secure. And if you're using a cloud vendor to supplement your processing power, inspect their security protocols to ensure they meet your organization's standards.
Train and validate enough
As discussed, accurate machine learning happens when your AI solution is fed huge amounts of good data. Make sure your training data is clean, representative, and a large enough data set to get the job done. If you're using historical data beware that there might be inherent bias. Having accurate inputs will ensure accurate outputs. In other words, garbage in garbage out!
After training your solution, you'll need to test and validate it. And because your solution is dynamic and learns over time, it needs to be validated periodically to ensure, for example, that it hasn't learned to discriminate against women.
Plan for your bot to "fail"
Half the people who attempt self-service end up transferring to an agent. Your bot will encounter many issues it can't resolve, so you should design a seamless elevation path to agent assistance. Being stuck in a conversation with a bot that keeps asking you to rephrase your question can be a little creepy. Don't do that to your customers! And don't make them repeat their issue to the agent. Ensure agents have easy access to everything that happened during the bot interactions. This will preserve the experience and make customers more likely to give the bot a second chance.
Pick the right use cases
Can your customers be disappointed by a missed flight, frustrated by a product defect, or devastated by a bad medical diagnosis? Regardless of your industry, there will be times when your customers need and deserve some empathy. Identify those use cases and include empathy in your bot design or better yet leave that to the agent.
Some AI solutions can detect customer sentiment. This ability can be used to program bots to respond with empathetic statements or transfer customers to agents if they are frustrated or upset. Organizations should determine if their AI bots will be handling any sensitive interactions and design their bots to respond appropriately.
Establish an ethics board
Having a formal AI ethics board will help your business maintain ethics and remove bias. The board should be composed of people from a cross-section of functional areas, such as IT, legal, product management, and customer service. You might also consider including external members such as customers and professional ethicists.
The ethics board will establish governance standards and processes. Not only can they provide ethics oversight; they can also provide transparency to how AI is used by the organization. Their feedback to developers, executives, and other stakeholders will be valuable input for strengthening ethical practices and data security.
Artificial intelligence shouldn't be creepy
AI can yield significant benefits when it's used properly and ethically. Applying AI in the contact center can improve accuracy, efficiency, and the customer experience. If your organization doesn't use AI yet, it's probably just a matter of time. Be sure to consider ethics and data security beginning Day 1 of your project. Designing your solution right and putting good standards and governance in place will help ensure your solution isn’t creepy.
Ensuring data security and establishing an ethics board are both AI best practices. For more tips to make your artificial intelligence effort a success in your call center, download our complimentary eBook, Best Practices for Applying AI in the Contact Center.
And read Solving for the Human Side of AI to learn more about how AI impacts contact center transformation.